AI-driven automation enhances server management services with smarter monitoring, proactive maintenance, stronger security, and improved efficiency. Instead of depending on manual processes, AI now automates operations, detects issues, and responds automatically, boosting efficiency and reliability.
What It Means:
Without relying on manual procedures, AI – driven automation uses technologies to:
- Watch server health and performance continuously.
- Predict and prevent issues before they happen.
- Fix problems or take corrective actions without human intervention.
- Optimize resources dynamically.
- Enhance security.
Why AI plays a key role in Server Management Services:
Below is a comparison table showcasing how AI-driven and traditional server management workflows differ:
| Aspect | Traditional Server Management | AI-Driven Server Management |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Manual, rule-based, fixed processes | Automated, adaptive, data-driven |
| Intervention | Heavily reliant on human oversight and manual fixes | Reduced human intervention, automated corrective actions |
| Monitoring | Periodic or reactive monitoring | Continuous, real-time monitoring and anomaly detection |
| Response to Issues | Reactive, often after problem occurrence | Proactive, detecting and resolving before failures |
| Scalability | Limited; scaling requires proportional resource increase | Highly scalable with dynamic workload balancing |
| Data Analysis | Basic logs and alerts | Advanced analytics with root cause analysis and event correlation |
| Error Rate | Higher due to manual processes and delayed responses | Lower with automated detection and remediation |
| Security | Traditional security tools, slower threat response | Real-time threat detection and adaptive security |
| Resource Optimization | Static allocation, less efficient | Dynamic resource allocation based on demand |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost reduction mainly from labor savings | Greater cost savings from optimization and predictive maintenance |
| Learning and Improvement | Static processes, limited learning | Continuous learning from operational data to improve accuracy and efficiency |
| Deployment Speed | Manual setup and configuration | Automated and faster deployment |
Overview of AI-driven automation for server management services:
Early Detection and Preventive Maintenance:
AI constantly monitors server health, analyzes logs, performance metrics and historical data to check if there are any anomalies. It foresees any hardware or software failures before its occurrence. This preventive action reduces unplanned downtime and supports timely maintenance to maximize server lifespan.
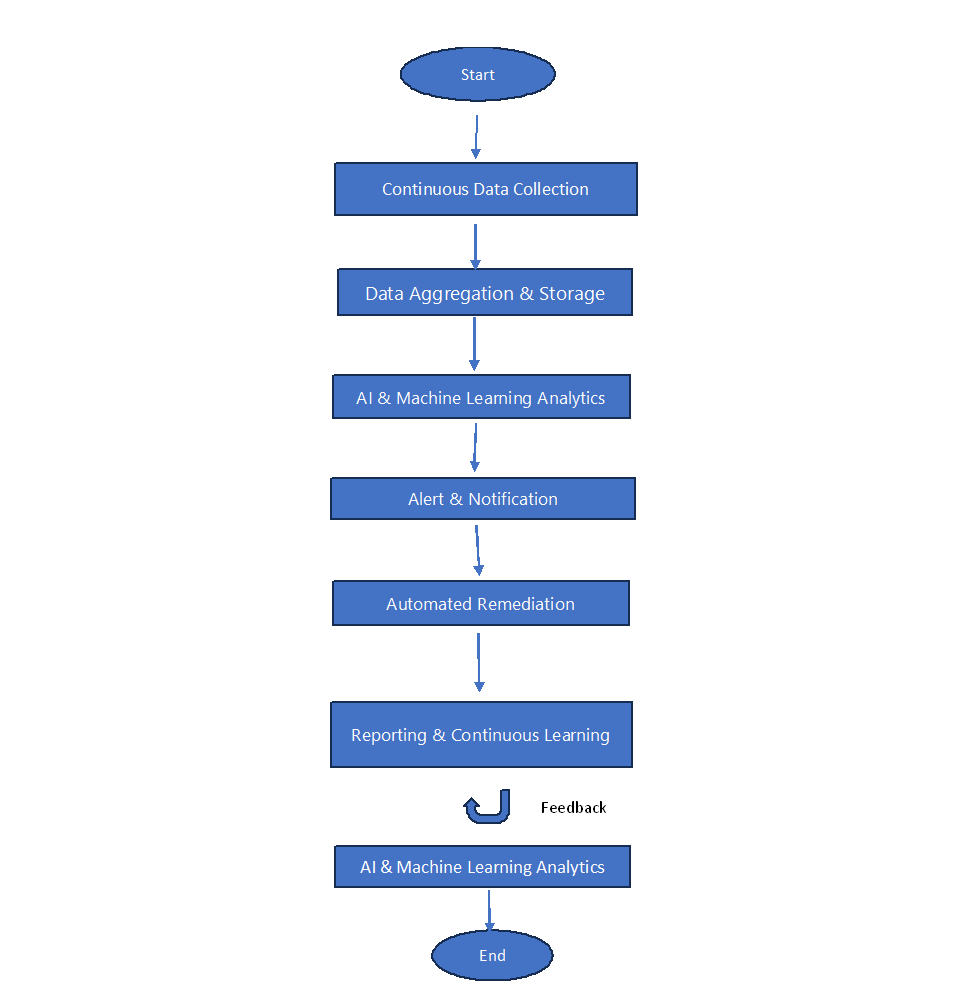
This diagram highlights the key stages:
AI agents does a continuous collection of server logs, performance metrics, hardware/software conditions and past data.
AI and machine learning process the data to identify if there are any anomalies and predict failures.
The system automatically generates notifications when it detects an issue.
The system triggers automated corrective actions to resolve issues.
The system reports results and feedback into the AI system to improve predictions and enable preventive measures.
Advanced server health monitoring tools such as ManageEngine OpManager, SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor (SAM), and open‑source platforms like Nagios, Zabbix, and SigNoz, analyze operational data and integrate AI‑driven insights.
Here are few pictorial representations:
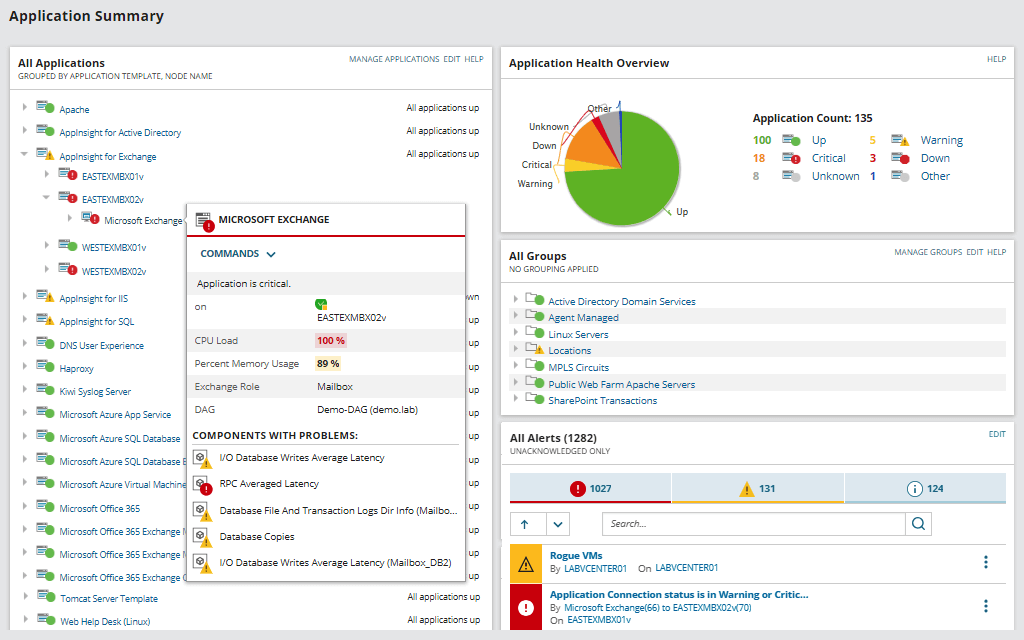
Graphical representation seems to be as shown:
Automated system setup and patch deployment
AI-enhanced automation frameworks guarantee consistent server configuration and secure patching thereby reducing manual mistakes. Thus, uniform standards enhance security and improves operational reliability which is very much useful in server management services.
How can this be done ?
Automated frameworks check server configurations versus standards and automatically fix discrepancies to ensure consistency and compliance without manual intervention.
Tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef automate server setup using predefined configuration scripts (Infrastructure as Code) to ensure identical, standards‑compliant servers.
AI-powered systems scan server environments to detect missing or outdated software patches.
Some notable tools include Automox, NinjaOne AI Patch Intelligence, ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus, GFI LanGuard, BatchPatch. Other tools like Atera, ITarian, and Miradore also integrate AI or automated policies for patch lifecycle management.
Automation tools schedule and deploy patches via plans to test, apply updates, minimize downtime, and reduce manual work.
AI analyzes patch effects and automatically halts or reverts updates if it detects problems, preventing disruptions.
AI-driven patch management platform Algomox automates and optimizes scheduling, deployment, risk assessment, rollback, and compliance tasks. Algomox reshapes patch management by assessing patch risks, intelligently scheduling updates, and delivering automated rollback functions to maintain system reliability.
AI-driven resource allocation and scalability
AI continuously adjusts workloads across CPUs, memory, and storage to optimize resource use, boost performance, and cut costs.
How can this be done ?
AI systems continuously monitor a wide range of system metrics and workload distributions, making real-time adjustments to resource allocation based on current demands. These systems analyze variables to fine‑tune resources, prevent bottlenecks, and redistribute underutilized ones for consistent high performance.
Also, AI uses historical data and workload patterns to forecast upcoming increases or decreases in resource demand. AI uses machine learning to scale resources up or down based on current demands for efficiency and performance.
AI-powered algorithms identify the best allocation of tasks and data by considering factors such as latency, hardware capabilities, and operational costs. They distribute workloads and place data‑heavy tasks near storage to improve performance and reduce delays.
AI agents function within the boundaries of business-specific policies, automatically identifying conflicts and suggesting resource reallocations when necessary. They use genetic and evolutionary techniques to improve allocation strategies by learning from outcomes and collaborating to enhance decisions.
AI models for resource optimization are regularly refreshed with new data and feedback, improving their precision over time. These systems continuously adapt to evolving requirements, market dynamics, and business strategies, maintaining efficiency and effectiveness.
A variety of AI-powered tools are used for optimizing resource utilization and workload adjustment across CPUs, memory, and storage. These tools typically feature real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making for resource allocation.
Epicflow: Epicflow uses machine learning and predictive analytics to forecast resource needs, analyze workloads, identify potential bottlenecks, and recommend the best task assignments. Features include a Future Load Graph, competence‑based allocation, and what‑if simulations to anticipate demand and test project changes.
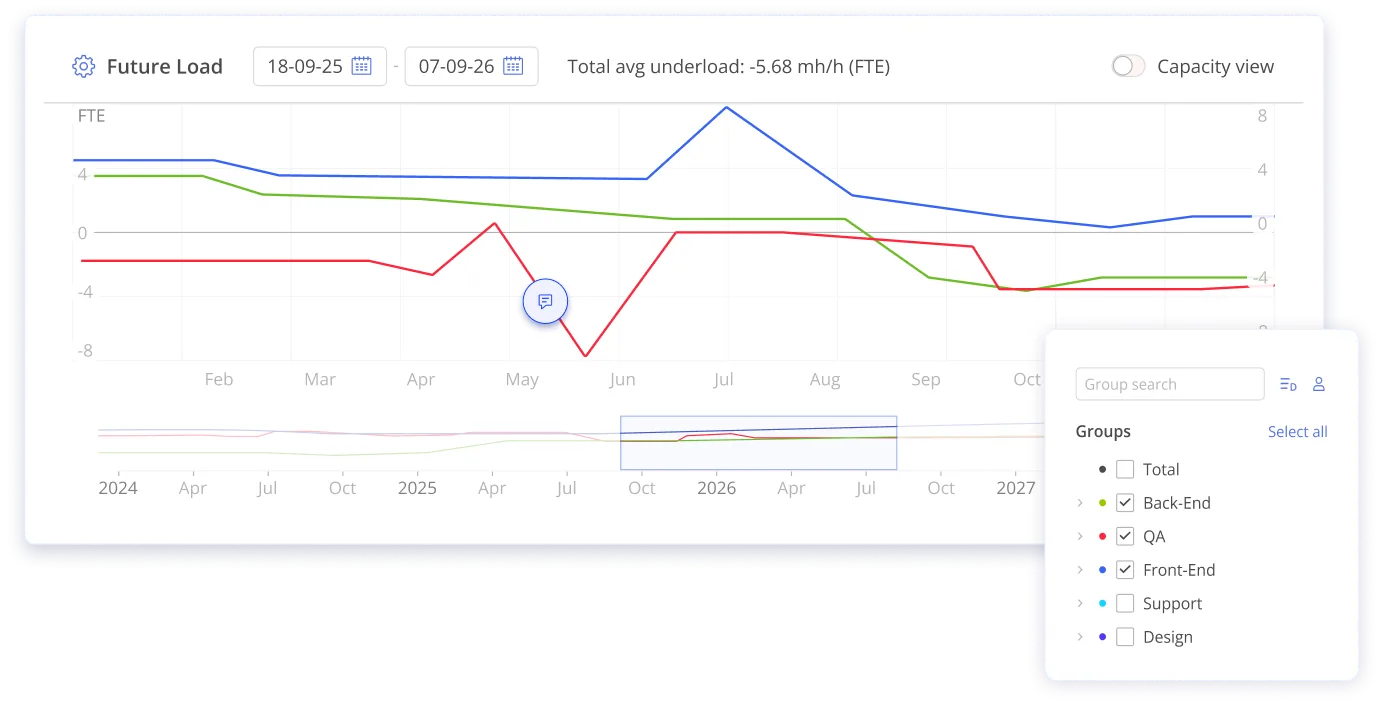
Enhanced Security:
AI systems monitor activity and logs to detect threats and respond in real time more quickly and reliably than manual methods.
How can this be done ?
Machine Learning (ML): AI trains machine learning models on large datasets to learn normal and harmful activity patterns and define standard behavior. This knowledge helps the system identify irregularities and unusual actions that indicate cyber threats, including unknown zero-day attacks. AI uses machine learning to classify risks and continually improve its threat detection and response strategies.
Behavioral Analytics: AI analyzes patterns to build baselines of typical user and system activities for detecting anomalies. It detects deviations from baselines and triggers alerts for potential risks like insider threats, unauthorized access, and ongoing attacks.
Real-Time Monitoring and Correlation: AI-powered security systems continuously surveil network traffic, endpoints, cloud resources, and user behaviors without experiencing fatigue, maintaining nonstop vigilance. They correlate and analyze diverse data to detect complex cyberattacks that isolated examination would likely miss.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI uses advanced techniques to process unstructured data like reports, logs, and emails, identifying malicious intent and contextual clues. This analysis improves threat detection by extracting insights from complex data, helping security systems understand risks and respond effectively.
Deep Learning: AI uses neural networks to identify complex patterns within network traffic and malware behaviors. By analyzing data at multiple levels, these systems detect subtle compromise signs, enabling early threat and anomaly identification.
Anomaly Detection Algorithms: AI uses time-series and advanced techniques to detect unusual activities like irregular logins or unexpected file access in real time. AI continuously analyzes sequential data to detect patterns and anomalies, allowing it to rapidly identify deviations from established norms. This capability enables prompt detection and response to potential security incidents, minimizing risk and impact in real time.
Threat Prediction and Risk Scoring: AI analyzes historical data and patterns to forecast potential attack targets and assign risk scores to various activities. Security teams prioritize incidents effectively by focusing on critical risks. They detect threats early and strengthen their security posture through proactive management of high-risk scenarios before escalation.
Automated Alerts and Response: AI-powered systems detect risks and immediately notify security teams. They also automatically initiate mitigation procedures, which significantly reduces response times and minimizes potential damage. Automation swiftly contains and remediates threats while enhancing overall security effectiveness.
Leading AI-Powered Security Tools
| Tool | Key Capabilities |
|---|---|
| SentinelOne Singularity | Endpoint protection with autonomous threat detection and automated mitigation. |
| Darktrace | Self-learning AI for detecting threats by modeling normal user and device behavior. |
| Exabeam Advanced Analytics | Machine learning-driven detection, investigation, and automated response. |
| Rapid7 InsightIDR | User behavior analytics and threat detection with automated workflows. |
| CrowdStrike Falcon | Endpoint detection, gathering and analyzing trillions of events weekly. |
| Fortinet FortiAI | Automated threat detection and investigation layered on existing security measures. |
| Cynet 360 | Autonomous breach protection and remediation. |
| Vectra Cognito | Network analytics for identifying hidden cyberattack patterns. |
| Microsoft Defender for Business | AI-led antivirus, real-time endpoint defense, automatic investigation. |
How these tools work?
AI-driven security systems process immense volumes of data from network traffic, access records, and user activities. They use advanced algorithms to recognize both known and unknown attack methods. These systems detect irregular behavior and alert security personnel or automatically contain threats by isolating devices and blocking access.
Organizations rely on AI-powered security tools for faster, smarter, adaptive defenses against cyber threats—advantages manual monitoring cannot match. Hence, these AI-powered security tools prove to be highly useful for server management services.
Below are the images of few tools that are mentioned in the table.
SentinalOne Singularity Tool:
Singularity Platform Tool:
Intelligent Threat Detection and Automated Resolution:
AI platforms detect incidents real-time, analyze root causes, and initiate fixes like restarts or reallocation. This minimizes human involvement and speeds up problem resolution.
How can this be done?
AI uses data analysis, machine learning, and automation to monitor systems real-time, correlate events, and initiate fixes like restarts or reallocation. AI thus reduces human intervention and speeds incident recovery which is helpful for server management services.
How AI Detects Incidents:
AI systems use machine learning to continuously analyze network traffic, logs, and user activities, spotting unusual behaviors that signal threats.
Unlike rule-based approaches, these platforms dynamically learn from data, detect unknown issues and zero-day attacks, and generate alerts upon finding anomalies.
Root Cause Analysis by Event Correlation:
AI automatically links events from logs, telemetry, and user actions to speed up root cause analysis and identify incident causes. It uses pattern recognition and analytics to connect events, reconstruct attack timelines, prioritize threats, and diagnose incidents faster than manual methods.
Automated Fixes and Resolution:
AI systems detect incidents, determine causes, and execute actions like restarts, isolation, blocking, or patches without human intervention. Platforms like SOAR and intelligent AI solutions integrate automated workflows. They resolve problems swiftly and reduce system downtime.
What are the Key Benefits ?
Speed: AI automation detects threats and resolves issues swiftly, often before human teams intervene. AI continuously monitors systems, processes alerts immediately, executes remediation workflows, and streamlines incident lifecycles. It cuts manual diagnostics and enables rapid fixes..
Accuracy: AI-driven triage and analytics filter alerts intelligently, prioritize genuine threats, refine detection accuracy, reduce false positives, and minimize human errors. Security teams focus on critical issues, ignore benign activities, and improve incident response quality and efficiency.
Proactivity: AI analyzes past events, continuously refines detection models, forecasts future incidents, and prevents them. It uses machine learning to identify patterns, predict threats, and implement proactive measures that reduce risks before problems arise. AI continuously learns and improves threat detection accuracy and effectiveness over time.
Reduced Human Involvement: Automation manages routine tasks like ticket creation, prioritization, and resource distribution. Human specialists then focus on complex problems. Automation reduces manual workload and ensures critical activities receive proper attention, enhancing efficiency.
Tools that are used to perfom this task:
AI-driven incident management tools detect threats real-time and correlate events for root cause analysis. They initiate fixes like restarts or reallocation, minimizing human intervention and accelerating resolution.
Some of them are:
CrowdStrike Falcon
An AI-driven, cloud-based endpoint security solution continuously monitors devices, automatically detects and contains threats. It seamlessly integrates with systems to provide comprehensive protection and rapid incident response.
Splunk Enterprise Security
It employs artificial intelligence to correlate complex data and analyze behavior patterns. And it automates response processes across complex environments.
IBM Security QRadar
A cloud-native scalable security information and event management system. employs AI to prioritize risk-based threats and analyze data real-time. It executes automated response workflows to swiftly mitigate security issues.
PagerDuty
It delivers immediate alerts and leverages AI to prioritize incidents. It automates escalations, remediation, and adoption in DevOps environments.
Palo Alto Cortex XDR
It delivers AI-powered analysis of user and system behaviors and automates root cause identification. It also coordinates real-time incident management to swiftly address security events.
Microsoft Sentinel
Microsoft builds Sentinel as a cloud-native SIEM solution for its ecosystem. It features AI-driven analytics and provides automated playbooks optimized for Azure, Office 365, and other Microsoft services. This platform unifies data collection, analysis, and response in a cloud-native system. It enhances threat detection and streamlines workflows for Microsoft technology users.

Rapid7 InsightIDR
Integrates AI-based user behavior analysis with automated responses. And it identifies and mitigates threats quickly..
Advantages of using tools:
These tools integrate with existing systems and use machine learning and AI models. They analyze large datasets, identify anomalies, correlate events, pinpoint root causes, and execute predefined or adaptive remediation actions automatically. This approach makes modern incident management proactive, scalable, and faster. Organizations can adopt these AI-powered platforms. They reduce downtime, improve operational resilience, and minimize manual efforts in incident detection and resolution.
Continuous Learning and Improvement:
AI models continuously learn from historical data and incidents. They improve prediction accuracy, sharpen response precision, and optimize strategies. This enables more efficient server management.
How can this be done ?
Teams implement AI continuous learning and improvement in server management services through several practical steps and technologies:
Teams gather extensive historical and live data for thorough analysis. They prepare data such as server logs, performance indicators, user interactions, and network activities.
Teams utilize machine learning algorithms to recognize trends and identify irregularities. They forecast potential hardware malfunctions, cybersecurity risks, and software problems before they arise.
Teams set up automated monitoring and alert systems. These systems promptly inform IT teams of irregularities and trigger predefined actions to minimize downtime.
Teams constantly update AI models by incorporating new data through ongoing training and feedback loops. They improve predictions and adjust to evolving server behaviors..
Teams use AI-powered robotic process automation (RPA) for routine server management tasks. It automates services like patching, updating, backing up, and scaling resources.
Teams apply predictive analytics for capacity planning and dynamic resource allocation. This enhances server performance and cost-effectiveness..
Teams incorporate AI into IT help desk and disaster recovery systems. This enables automatic issue resolution and simulates failure scenarios.
Organizations invest in a secure AI infrastructure with multi-factor authentication and encryption. They also train IT teams to proficiently manage AI tools.
Tools that are used to perfom this task:
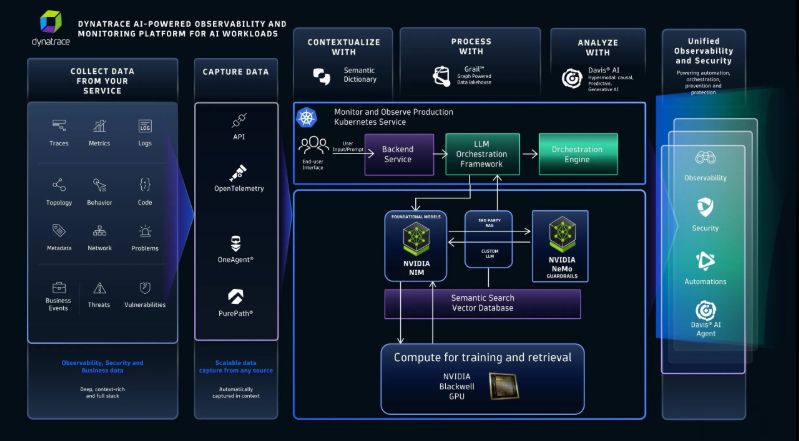
Dynatrace
An AI-powered intelligent monitoring platform, continuously observes servers, applications, and cloud infrastructure. It delivers real-time insights to ensure optimal performance and enable early detection of potential issues.

Datadog
A comprehensive monitoring and analytics platform, equips with AI functions. It detects anomalies, performs predictive analytics, offers real-time system insights, forecasts potential issues, and optimizes performance proactively..
Splunk AIOps
It employs machine learning to analyze data, prioritize alerts, identify issues early, and automate resolutions for efficient problem management..
New Relic
It provides comprehensive observability across the entire technology stack. This includes AI-enhanced monitoring that combines logs, metrics, and traces to enable proactive system management and issue resolution.
Julius AI
It delivers real-time insights and detects anomalies. And it monitors server performance effectively.

Watchwolf
An AI-driven server management app, includes an interactive AI conversation mode. It offers real-time monitoring and supports container management and SFTP transfers. This app enhances server oversight and operational efficiency using intelligent automation and integrated tools.
OpManager Plus
It applies AI-driven predictive algorithms to improve infrastructure monitoring and management. It identifies patterns and anomalies that signal potential failures, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.


Selector AI (AIOps)
Selector AI (AIOps) employs AI and machine learning to intelligently identify issues and quickly resolve them in network and server infrastructures. Thereby, it enhances operational efficiency and minimizes downtime..

Uses of the tools:
These tools integrate machine learning, predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, automation, and AI-driven insights. They support proactive server management.They automate repetitive tasks, forecast potential failures, and optimize the allocation of resources. These solutions scale across various business sizes. They enhance uptime, reduce the need for manual intervention, and improve the overall efficiency of IT teams.
Conclusion:
Key Benefits of AI-Enabled Automation Services:
Key Benefits of AI-Enabled Automation Services:
The system automates tasks to decrease manual workload and errors.
AI improves operational performance and server uptime.
Predictive maintenance and resource optimization deliver financial benefits.
The system monitors threats continuously and provides rapid responses to enable advanced security.
Increases its effectiveness in administering complex, large server environments.
To summarize, AI-enabled automation remodels server management services. It incorporates intelligence, predictive observations, and flexibility to improve reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness in server operations.







