With few boundaries and countless temporary cloud resources in the Microsoft Cloud, attackers can access your cloud environment if configurations are set incorrectly. As Azure evolves rapidly and businesses adopt it quickly, it’s easy to overlook steps and open your business to attacks. Here we go through issues by misconfiguration and how to fix them.
Allowing Excessive Access
Manage user access permissions
The most common mistake in Azure user access control is granting more permissions than needed for a job. Microsoft’s Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) allows detailed access control for Azure resources. Access is managed through role assignments, which enforce permissions. A role assignment includes a security principal, a role definition, and a scope.
- A security principal represents a person, group, or application requesting access to an Azure resource, which can then be assigned a role.
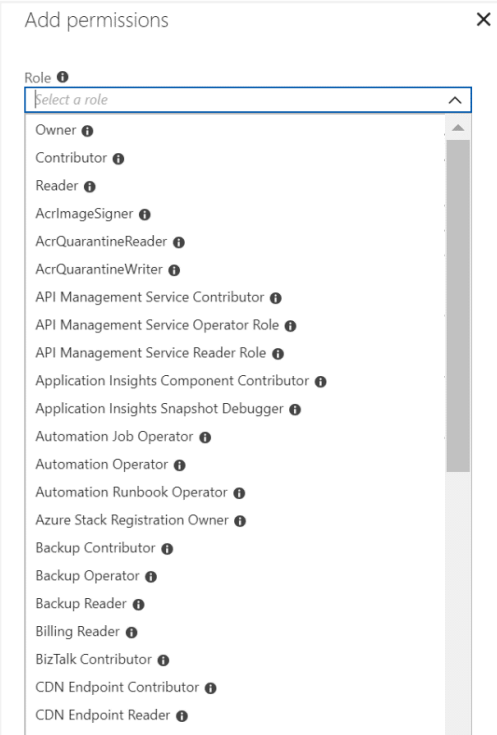
- A role definition is a set of permissions, often called a role, that specifies what actions can be performed, like read, write, or delete. Azure has four main built-in roles: Owner (full access), Contributor (manage resources but can’t grant access), Reader (view resources), and User Access Administrator (manage user access).
- After assigning roles, you can set a scope, where the access applies. In Azure, scopes can be set at different levels: subscription, resource group, or resource. Scopes follow a parent-child structure, where each child has only one parent. As a result, child scopes inherit permissions from their parent scope.
Limit access to the Azure AD portal
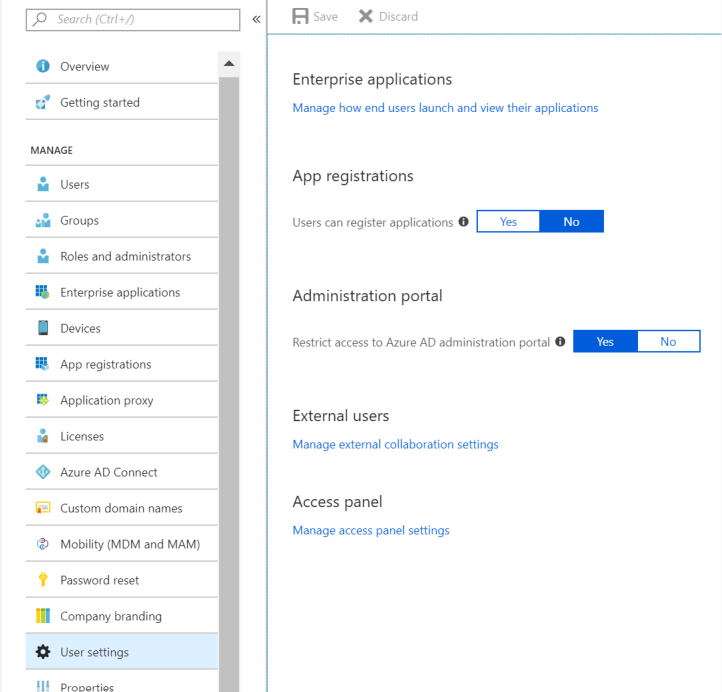
Restrict non-administrators from accessing the Azure AD portal to protect sensitive data. Follow the steps given below:
Step 1. Login into the Azure Portal.
Step 2. Go to Azure Active Directory.
Step 3. Go to Users settings.
Step 4. Ensure that Restrict access to the Azure administration portal is set to Yes.
Restrict guest access
To disable guest access follow the steps given below:
Step 1. Login into the Azure Portal.
Step 2. Go to Azure Active Directory.
Step 3. Go to Users settings.
Step 4. Go to External collaboration settings.
Step 5. Ensure that Guests can invite is set to No.
Xieles helps identify and solve Azure misconfigurations using best practices in cloud environments.!







